
A Future Response Model for HTTP Servlets
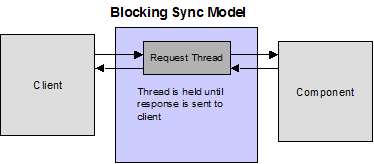
In general, WebLogic Server processes incoming HTTP requests and the response is returned immediately to the client. Such connections are handled synchronously by the same thread. However, some HTTP requests may require longer processing time. Database connection, for example, may create longer response times. Handling these requests synchronously causes the thread to be held, waiting until the request is processed and the response sent.
To avoid this hung-thread scenario, WebLogic Server provides two classes that handle HTTP requests asynchronously by de-coupling the response from the thread that handles the incoming request. The following sections describe these classes.
Abstract Asynchronous Servlet
The Abstract Asynchronous Servlet enables you to handle incoming requests and servlet responses with different threads. This class explicitly provides a better general framework for handling the response than the Future Response Servlet, including thread handling.
You implement the Abstract Asynchronous Servlet by extending theweblogic.servlet.http.AbstractAsyncServlet.java class. This class provides the following abstract methods that you must override in your extended class.
doRequest
This method processes the servlet request. The following code example demonstrates how to override this method.
public boolean doRequest(RequestResponseKey rrk)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest req = rrk.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse res = rrk.getResponse();
if (req.getParameter("immediate") != null) {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
out.println("Hello World Immediately!");
return false ;
}
else {
TimerManagerFactory.getTimerManagerFactory()
.getDefaultTimerManager().schedule
(new TimerListener() {
public void timerExpired(Timer timer)
{try {
AbstractAsyncServlet.notify(rrk, null);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, 2000);
return true;
}
}
doResponse
This method processes the servlet response.
| Note: | The servlet instance that processed the doRequest() method used to handle the original incoming request method will not necessarily be the one to process the doResponse() method. |
If an exception occurs during processing, the container returns an error to the client. The following code example demonstrates how to override this method.
public void doResponse (RequestResponseKey rrk, Object context)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
HttpServletRequest req = rrk.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse res = rrk.getResponse();
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
out.println("Hello World!");
}
doTimeOut
This method sends a servlet response error when the notify() method is not called within the timeout period.
| Note: | The servlet instance that processed the doRequest() method used to handle the original incoming request method will not necessarily be the one to process the doTimeOut() method. |
public void doTimeout (RequestResponseKey rrk)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
HttpServletRequest req = rrk.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse res = rrk.getResponse();
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
out.println("Timeout!");
}
Future Response Servlet
Although Oracle recommends using the Abstract Asynchronous Servlet, you can also use the Future Response Servlet to handle servlet responses with a different thread than the one that handles the incoming request. You enable this servlet by extending weblogic.servlet.FutureResponseServlet.java, which gives you full control over how the response is handled and allows more control over thread handling. However, using this class to avoid hung threads requires you to provide most of the code.
The exact implementation depends on your needs, but you must override the service() method of this class at a minimum. The following example shows how you can override the service method.
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, FutureServletResponse rsp)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if(req.getParameter("immediate") != null){
PrintWriter out = rsp.getWriter();
out.println("Immediate response!");
rsp.send();
} else {
Timer myTimer = new Timer();
MyTimerTask mt = new MyTimerTask(rsp, myTimer);
myTimer.schedule(mt, 100);
}
}
private static class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{
private FutureServletResponse rsp;
Timer timer;
MyTimerTask(FutureServletResponse rsp, Timer timer){
this.rsp = rsp;
this.timer = timer;
}
public void run(){
try{
PrintWriter out = rsp.getWriter();
out.println("Delayed Response");
rsp.send();
timer.cancel();
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
'엔터프라이즈 솔루션 > BEA WebLogic' 카테고리의 다른 글
| WebLogic에서 Inflight Transaction(진행중인 트렌젝션) 상태 모니터링 하기 (0) | 2008.07.10 |
|---|